
Yes, as part of Pinscreen, we are taking a step further and targeting at digitizing realistic 3D avatars from a single photograph, which will allow anyone to create their own digital selves in seconds and incorporate into any game and VR application.
Which takes us out of your lab and into your company. Plus, since our early work using depth sensors showed how compelling faces can be animated without complex mocap systems, solutions that only require pure RGB cameras have been introduced shortly after, and those technologies have since then been adopted widely in the consumer space such as in mobile phone apps, face recognition systems, VR headsets, and so on. We won't need to use the Light Stage to do this soon.
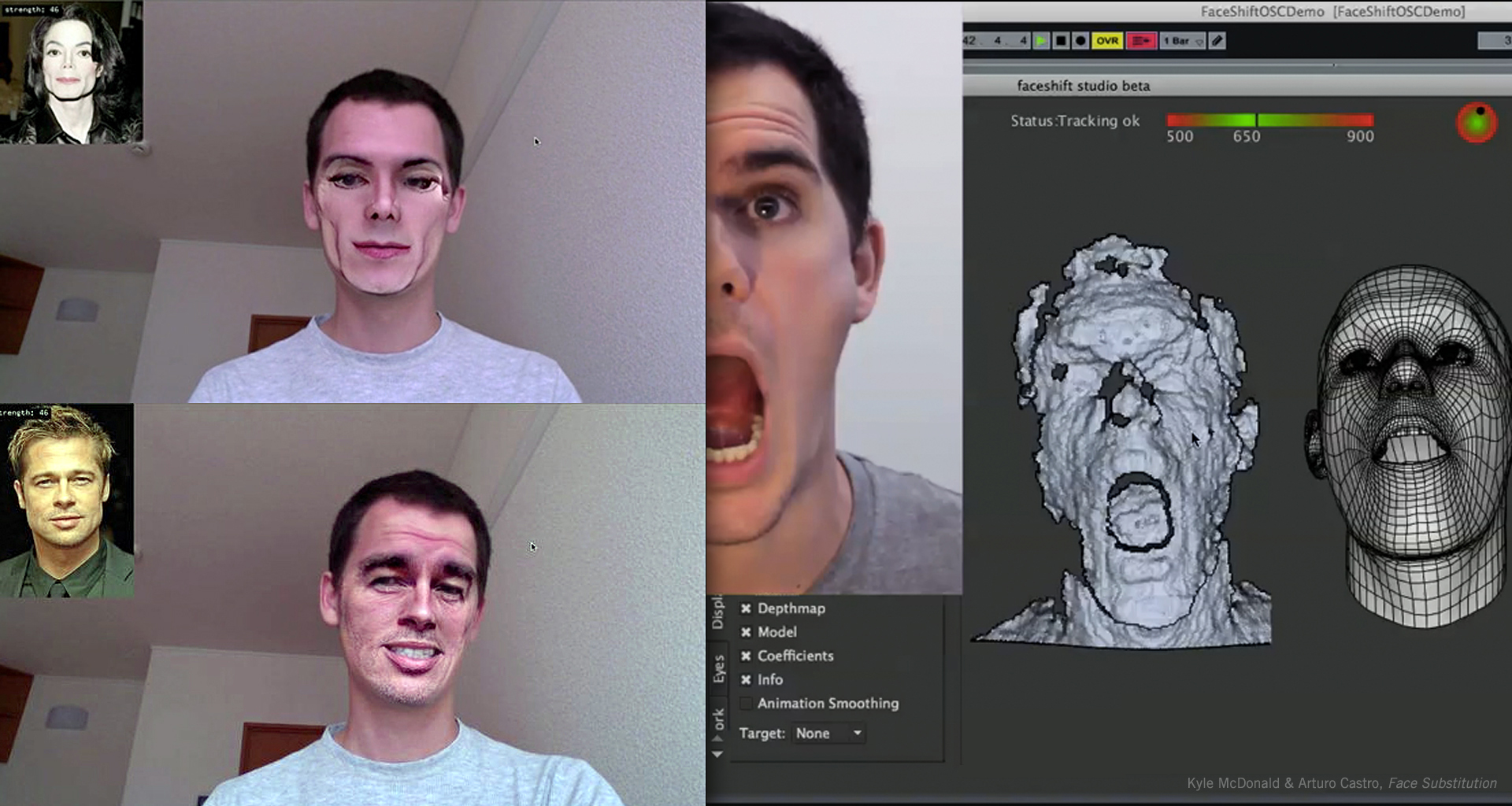
Without the use of markers, as with conventional motion capture, or Light Stage capture, which we saw digitize Robin Wright in The Congress ? Exactly. Since human faces are one of the most complex things to animate, we applied our algorithm to the performance capture of human faces and enabled the ability to track complex facial expressions in real time.

Our research consisted of recovering dense surface motions from this data, so that a dynamic 3D model of a real object can be generated similar to those modeled and animated by an artist.Īnd you were able to do this, even with human faces? Right. While depth sensors are fairly accurate in measuring the world, they only capture part of the information and the raw data is unstructured. But, I thought, if a sensor can see the world in 3D and could digitize content directly, wouldn't that change the way we create animations? one of the hardest things to create was a realistic animation of a digital human since it involves complex motion capture devices and artists. That was the early days of visual effect in the 90s, I remember how people were blown away by visual effects done by companies such as Industrial Light & Magic, where I later worked, on movies like Terminator 2, Jurassic Park, and so on.Ĭan you explain why your research on geometric capture of human performances moves us beyond today's clunkier methods, such as using markers, motion-capture, etc.? When I started my PhD at ETH Zurich, real-time 3D sensors-similar to Microsoft's Kinect, but not yet commercialized-were just invented and only available in research labs.
Faceshift studio crash software#
When PCs became available, I started to play with more sophisticated graphics programming and used professional 3D modeling software to create my own CG renderings and animation. When did you first get interested in computer graphics, tech, and creating virtual humans? When I was a kid, I had a Commodore 64, and learned BASIC to enable me to put pixels on the screen. PCMag called him at his lab in Playa Vista, California, not far from the Google campus, to learn about his virtual humans and see how he brings them to life.ĭr. Today, he's an assistant professor of computer science, director of the Vision and Graphics Lab, and CEO of an AR startup, Pinscreen. Li earned his doctorate in computer science at ETH Zurich, and became a research lead at Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) before joining the University of Southern California (USC).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
